Disclosure: Certain information contained herein has been obtained from third party sources and such information has not been independently verified by Stonehearth Capital Management. No representation, warranty, or undertaking, expressed or implied, is given to the accuracy or completeness of such information by Stonehearth Capital Management or any other person. While such sources are believed to be reliable, Stonehearth Capital Management does not assume any responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of such information. Stonehearth Capital Management does not undertake any obligation to update the information contained herein as of any future date. The content is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered personal financial advice. GE’s benefits and policies may change over time, and while we strive to keep this information as up to date as possible, we encourage you to confirm the latest details directly with GE or your HR department regarding your specific retirement and benefit options.
GE Aerospace Retirement & Benefit Planning
You’ve worked hard. Now it’s time to turn your GE benefits into a confident retirement strategy.
Here is a central resource for GE employees and our advisory team to understand, evaluate, and plan around the full spectrum of GE Aerospace retirement and benefit options.
Stonehearth Capital Management is not affiliated with, endorsed by, or sponsored by GE Aerospace. We are an independent financial advisory firm that has experience working with GE Aerospace employees and their retirement benefits.
Recent update: We recently learned that effective 1/1/2025 the pension is being administered by Fidelity and they can be reached M-F at 877-554-3777
Employer Retirement Plan (401k, 403b, etc)
GE Retirement Savings Plan (RSP)
This section outlines the structure and strategic considerations of the GE Retirement Savings Plan (RSP), including matching contributions, Roth opportunities, and rollover options.
-
Maximum employee contributions (2025):
Under 50: $23,500
Catch-up if 50+ by yearend: $7,500 catch-up is funded throughout entire year.
Super Catch-up (in place of catch-up) if 60-63 by yearend: $34,750
Eligibility: All employees; no waiting period
Contribution Range: 1%–30% of pay (restricted automatically if you are a Highly Compensated Employee, aka HCE).
Employer Match: 50% of up to 8% of employee contributions
Company Retirement Contribution (CRC): 3%, deposited in January (if employed on Dec. 15th of previous year)
Max Employer Contribution: 7% (really strong)
Vesting: 3 years of RSP service
Platform: Fidelity
Brokerage Link: Available
In-Service Rollover: Available
Mega Backdoor Roth: Available (amazing benefit). After-tax contributions begin automatically after initial contribution threshold of $23,500 is met. Contributions to after-tax bucket occur at the same time as catch-up contributions, if applicable.
-
✅ Contribute at least 8% to receive full employer match
✅ Max out after-tax if pre-tax/Roth are maxed
✅ In-service rollovers expand investment flexibility
✅ Use Brokerage-Link for diversification
For illustrative purposes only.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
GE HSA, HRA & FSA
GE offers a suite of health-related accounts designed to reduce taxable income and improve financial flexibility. These include the Health Savings Account (HSA), Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA), and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs). Each account type plays a distinct role in health and retirement planning, with varying rules for contributions, rollovers, and taxation.
-
🟢 Health Savings Account (HSA)
Eligibility: Only available if enrolled in GE Option 3 high-deductible health plan
Funding: Employee-funded via pre-tax payroll deduction
Rollover: Unused funds roll over indefinitely
Portability: Fully portable — account remains yours after separation
GE-specific:
Only available with Option 3 medical plan
Limited Purpose FSA can be used alongside HSA for dental/vision only
Contribution Limits (2025): Individual $4,150, Family $8,300, +$1,000 catch-up (age 55+)
🟠 Healthcare FSA & Limited Purpose FSA
Eligibility: Must be enrolled in Option 1 or 2 for Healthcare FSA;
Option 3 for Limited Purpose FSA (HSA-compatible)Funding: Employee-funded via pre-tax payroll deductions
Carryover: Some unused funds can roll over (subject to IRS limit, e.g., $640 for 2025)
Use Cases:
Healthcare FSA: Medical, dental, vision (Options 1/2)
Limited Purpose FSA: Dental/vision only (used with HSA)
Contribution Limit (2025): ~$3,200
🟣 Health Reimbursement Account (HRA)
Eligibility: GE-funded account available for Options 1 and 2
Funding: Employer-only contributions
Rollover: Unused funds roll over if remaining in same GE plan
Portability: Not portable — forfeited if leaving plan or company
🔴 Dependent Day Care FSA
Eligibility: Available regardless of medical plan
Funding: Employee-funded, $100–$5,000 annually (single or married filing jointly)
Rollover: None — “use it or lose it”
Taxation: Contributions reduce taxable income; must be used for eligible dependent care
-
✅ Max out your HSA contributions annually — this triple tax-advantaged account can act as a long-term healthcare nest egg and retirement supplement
✅ Enroll in the correct FSA for your medical plan — use a Healthcare FSA with Options 1 or 2, and a Limited Purpose FSA with Option 3 (HSA-compatible for dental/vision only)
✅ Avoid overfunding FSAs near retirement or job changes — unused balances can be forfeited if not rolled over or if you leave GE
✅ Spend your Dependent Day Care FSA by year-end — this account follows a strict “use it or lose it” rule with no rollover
✅ Stay in the same health plan if you want HRA funds to roll over — GE HRA balances only carry over when you stay enrolled in Option 1 or 2
✅ Use HSA funds to pay Medicare premiums after age 65 — including Part B, D, and Medicare Advantage (but not Medigap)
✅ Coordinate HSA contributions with spouse coverage — especially if they’re enrolled in an FSA or different health plan, which can limit HSA eligibility
✅ Prioritize HSA for long-term savings, not just annual spending — it’s one of the only tax-free vehicles for healthcare in retirement
✅ Stop HSA Contributions at Least 6 Months Before Medicare: To avoid IRS penalties for excess HSA contributions, you should stop contributing at least 6 months before you apply for Medicare.
✅ Understand tax reporting — FSAs reduce your W-2 income; HSA contributions appear on Form 8889; and HRA reimbursements are tax-free but require recordkeeping
Equity Compensation & Bonus Programs
GE Equity Compensation & Bonus Programs
GE offers a range of performance-based compensation to reward and retain top talent. These include Restricted Stock Units (RSUs), Nonqualified Stock Options (NSOs), and annual cash bonuses. While these can significantly increase total compensation, they also create complex tax implications, and should be coordinated with broader retirement, tax, and estate planning strategies.
-
📊 Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Eligibility: Broadly offered to leaders, key contributors, and executives
Vesting: Typically vests over 3–4 years
Taxation:
Taxed as ordinary income at vesting
Value reported on W-2
Subject to income tax and payroll tax (FICA)
Settlement: Delivered in GE stock; can be sold or held
Withholding: GE often withholds ~22–37% in shares for taxes
💼 Nonqualified Stock Options (NSOs)
Eligibility: Senior leaders, often Executive Band and above
Vesting: Typically over 4 years; exercisable up to 10 years
Taxation:
No tax at grant or vesting
Taxed at exercise on the “spread” (FMV – strike price)
Ordinary income + FICA; no AMT
Sale of Shares: Further capital gains tax if shares are held post-exercise
💰 Executive Incentive Bonus Programs
Structure: Annual cash awards based on company, business unit, or personal performance
Taxation: Fully taxable as ordinary income in the year received
Timing: Typically paid in Q1 of the following year
-
✅ Time RSU vests and NSO exercises during lower-income years when possible to reduce tax drag
✅ Review RSU withholding — additional tax payments may be required to avoid underpayment penalties
✅ Coordinate equity income with other large events (bonuses, pension payouts, Roth conversions) to manage brackets
✅ Use charitable strategies (donor-advised funds or gifting appreciated stock) to offset high-income years
✅ Diversify if GE stock represents a large portion of net worth or retirement assets
✅ Understand expiration timelines on NSOs — unexercised options can expire worthless after 10 years
✅ Work with a tax advisor before selling exercised options or post-vesting RSUs to avoid surprise tax bills
Deferred Compensation Plans
GE Nonqualified Deferred Compensation (NQDC) Plans
GE offers select senior leaders the ability to defer compensation through nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plans — most notably the AEIP (Annual Executive Incentive Plan) and IC Plan (Incentive Compensation). These programs are designed to help executives manage taxable income, smooth cash flow, and plan strategically for retirement or career transitions. Unlike qualified plans (e.g. 401(k)), these are unfunded and unsecured, meaning benefits are backed only by GE’s corporate promise.
-
🟢 AEIP (Annual Executive Incentive Plan) Deferral
Eligibility: Executive Band and above
Deferral Options:
Elect to defer all or part of your annual bonus
Election Timing:
Must be made in the calendar year prior to when the bonus is earned
Payout Options:
Typically allow for lump sum or installments (up to 10 years)
Payouts begin at a specified future year or following termination
🔵 IC Plan (Long-Term Incentive Compensation) Deferral
Eligibility: Typically for senior executives receiving long-term performance awards
Deferral Mechanics:
Elect to defer part or all of eligible long-term cash awards
Vesting: Subject to continued service and performance conditions
Distribution: Lump sum or installment, typically post-termination
⚠️ Plan Characteristics (Both Plans)
Unfunded & Unsecured: Subject to GE solvency
No Early Withdrawals: IRS Section 409A strict rules apply
FICA Tax Timing: Assessed upon vesting, not distribution
Creditor Risk: Assets remain part of GE’s general assets
-
✅ Use deferrals to manage tax brackets — ideal for high-income years with RSUs, bonuses, or stock option exercises
✅ Align distributions with retirement cash flow — consider 5- or 10-year installments to replace salary
✅ Plan around Medicare IRMAA and other income-based thresholds (especially in early retirement)
✅ Elect deferrals carefully — once submitted, elections are irrevocable and subject to IRS 409A rules
✅ Model future tax scenarios — avoid “income stacking” from pensions, NQDC, RSUs, and IRA withdrawals all in the same year
✅ Understand corporate risk — benefits are dependent on GE’s financial strength; diversify where possible
✅ Revisit elections regularly — particularly if you experience a promotion, career change, or early exit
Life Insurance
GE Basic, Supplemental & Executive Life Insurance
GE provides a multi-tiered life insurance program for employees, including Basic Life, Supplemental Group Life, and a now-frozen Executive Life Plan for legacy senior leaders. These benefits help protect your family’s financial security during your working years and — in some cases — into retirement. Understanding what you’re covered for, what’s optional, and what happens at retirement is key to maximizing the value of this benefit.
-
🟠 Basic Life Insurance
Coverage: 2× base salary
Cost: Paid by GE; imputed income may apply over $50,000 in coverage
Eligibility: All benefits-eligible employees
Taxation: Premiums above $50K are reported as taxable income (per IRS rules)
🔵 Supplemental Group Life Insurance
Coverage Amount: 1× to 10× base salary (employee-paid)
Enrollment Window: Must elect within 63 days of hire, or during a life event or open enrollment
Spouse Coverage: Up to $100,000
Child Coverage: Up to $10,000
Conversion Options: Available at separation or retirement, subject to plan rules
Underwriting: May be required for late elections or higher amounts
⚫ Executive Life Insurance (Frozen Plan)
Eligibility: VPs and above hired before plan freeze (varies by year and division)
Coverage:
VPs: $1 million
SVPs: $2 million
Growth: Benefits accrue 4% annually until age 60
Ownership: Participant-owned policies (not group-term)
Cash Value: Policies may build cash value and eventually become paid-up
Taxation: Generally not taxable unless transferred or surrendered with gain
-
✅ Keep beneficiary designations updated — especially after marriage, divorce, or family changes
✅ Monitor imputed income from Basic Life if you’re over $50K in coverage — it’s often overlooked in tax planning
✅ For Supplemental Life, review portability and conversion options well before retirement to avoid gaps in coverage
✅ Consider trusts for high-net-worth individuals — transferring life insurance to a trust can help with estate tax mitigation
✅ Executive Life Plan participants should:
✅ Regularly check policy performance and cash value
✅ Avoid policy loans or missed premium payments that can erode long-term value
✅ Consider funding estate liquidity or gifting strategies with the policy
Parental Leave
GE Parental Leave
GE supports growing families with a paid parental leave program that applies to all eligible parents — including birth, adoptive, and surrogate parents. The policy is designed to offer both financial protection and the flexibility to bond with a new child during the critical early weeks. Parental leave is distinct from disability leave and is available to all parents regardless of gender or caregiver role.
-
🟠 Paid Parental Leave
Eligibility: Available to employees with at least one year of GE service
Duration: Up to 10 weeks of fully paid leave
Applies To:
Birth mothers (separate from medical/disability leave)
Non-birth parents
Adoptive parents
Surrogacy and foster placements (case-dependent)
Compensation: 100% of base pay for the duration of the leave
Coordination: May be taken separately or in combination with other leaves (e.g., disability, vacation, FMLA)
Job Protection: Leave is generally job-protected, consistent with FMLA and company policy
Scheduling: May be flexible; check with HR for options to split or delay portions of leave if needed
-
✅ Plan timing around your work calendar — especially for bonus cycles, annual reviews, or high-demand project periods
✅ Coordinate parental leave with disability coverage — birth mothers may receive disability (SCP) first, then parental leave
✅ Confirm eligibility and job protection status early — especially if you are within your first year of employment
✅ Review your benefits during leave — ensure continued health insurance, life insurance, and retirement contributions remain active
✅ Consider splitting leave time — if allowed, breaking leave into blocks may support smoother transitions or shared caregiving responsibilities
✅ Update beneficiary designations and guardianship documents — new family members often trigger estate planning updates
✅ Leverage tax credits — costs related to adoption or dependent care may qualify for tax credits or FSA reimbursement
Disability Insurance
GE Disability Insurance Coverage
GE provides income protection for employees who are unable to work due to illness, injury, or medical conditions. This includes Short-Term Disability through the Salary Continuation Program (SCP) and Long-Term Disability Insurance (LTDI). These benefits are designed to replace a portion of your income during both temporary and extended periods of disability, ensuring financial stability while you recover or transition.
-
🟠 Short-Term Disability (Salary Continuation Program – SCP)
Eligibility: All benefits-eligible GE employees
Coverage: Replaces 100% of base salary
Duration: Up to 26 weeks of full pay
Start Date: Begins immediately upon approved disability claim
Cost: GE-paid benefit — no employee contribution
Medical Certification: Required for claim approval
🔵 Long-Term Disability Insurance (LTDI)
Eligibility: Automatically provided for eligible employees
Coverage: Replaces 50% or 60% of base salary (based on plan election)
Waiting Period: Begins after SCP ends (typically after 26 weeks)
Duration: Continues as long as you remain disabled and meet eligibility
Taxation:
If premiums are GE-paid, benefits are taxable
If employee-paid (after-tax), benefits may be tax-free
Offsets: May be reduced by Social Security Disability, Workers Comp, or other income
-
✅ Understand income replacement limits — even with 60% LTDI, there may be a gap if you rely on bonuses, stock, or commission
✅ Build an emergency fund equal to 3–6 months of living expenses — to cover any approval delays or out-of-pocket needs during SCP
✅ High earners should evaluate private disability coverage — GE’s LTDI caps may not fully replace compensation above the plan limits
✅ Coordinate disability income with Social Security Disability — if you anticipate a long-term claim, apply early to avoid benefit delays
✅ Know how disability impacts other benefits — vesting for pensions, stock options, and NQDC may pause or terminate during long-term leave
✅ Review taxability of benefits — if GE pays the premiums, LTDI benefits are taxable, which reduces net income
✅ Prepare for transitions — If you move from SCP to LTDI, reevaluate your budget and benefit elections, especially life and health insurance continuity
Pension/Retirement Income
GE Pension Plan
The GE Pension Plan is a traditional defined benefit plan that provided eligible GE employees with monthly retirement income based on years of service and earnings.
-
Status: Frozen as of Dec 31, 2020
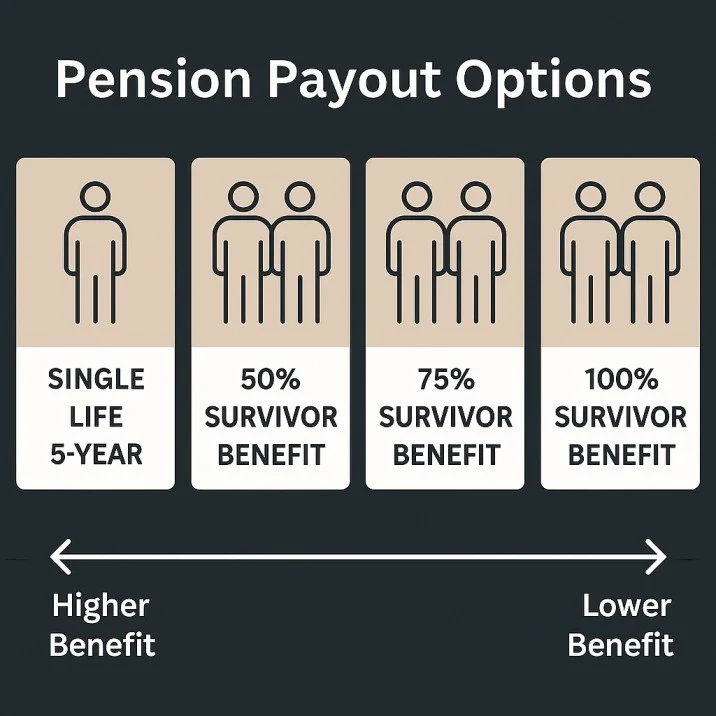
Payout Options: Monthly Income (no lump sum option)
Monthly Survivorship Options:
Single: 5-Year Certain
50%, 75% or 100% Survivor Benefit
-
✅ Married couples should consider survivor options. Most family expenses fall by 25% after first spouse passes, making 75% survivor benefit a good place to start the conversation.
✅ Married couples should consider single, 5-year certain WITH a life insurance policy.
For illustrative purposes only.
GE PPA/VPA
The Personal Pension Account (PPA) and Voluntary Pension Account (VPA) are cash balance-style pension plans GE introduced to modernize retirement benefits. Instead of traditional pension formulas, these accounts grow over time based on interest credits and pay credits tied to your service and compensation.
-
Status: Frozen as of Dec 31, 2020
Payout Options: Lump Sum or Monthly Income
Lump Sum Options:
Withdraw (fully taxable, 20% mandatory withholding)
Direct Rollover (retains tax deferred status)
Monthly Survivorship Options:
Single: 5-Year Certain
50%, 75% or 100% Survivor Benefit
-
✅ Compare lump sum vs. monthly income
✅ Retirees with children often (but not always) favor lump sum to increase odds their children will get something
✅ Align pension with Social Security and withdrawals
✅ Account for monthly supplements in cash flow
For illustrative purposes only.
GE Pension Supplement
The GE Pension Supplement is a temporary monthly benefit paid in addition to your regular GE pension. It’s designed to help bridge the income gap between retirement and the time you begin receiving Social Security.
-
Status: Frozen as of Dec 31, 2020
If you joined GE after the freeze or didn’t meet age/service rules by 1/1/21, you will not receive this benefit.
Begins at retirement and ends when you reach 80% of your estimated Social Security benefit.
Paid automatically if you qualify and elect a monthly pension.
Survivor benefit election has no impact on amount received.
Formula:
Regular: $31 × years of service, plus
Special: $375/month
-
✅ Don’t Overlook the Sunset
This benefit disappears at age 62—or earlier—so plan for an income drop when it ends.✅ Claiming Social Security Early? Think Twice
Taking Social Security at 62 may align with the supplement’s end, but claiming too early can lock in a lower lifetime benefit.✅ Bridging or Trapping?
This supplement helps bridge the gap to age 62, but if not planned for, it can trap retirees into spending more early and facing a future income gap.
For illustrative purposes only.
GE Executive Retirement Benefit (ERB)
The GE Executive Retirement Benefit (ERB) is a supplemental, non-qualified pension designed to enhance retirement income for GE executives whose total compensation exceeds IRS limits applied to traditional pension formulas. It’s meant to restore benefits lost due to compensation caps and reward long-term leadership.
-
Offered to GE employees in executive or senior leadership roles (typically Career Band E or above).
Pays a monthly benefit designed to bring the total retirement income (including base pension) in line with original formulas that excluded IRS limits.
Includes two parts:
Part I (Supplementary Annuity Benefits) – Frozen as of 12/31/2020; no new accruals after this date.
Part II (Annual Installment Benefits) – Replaced Part I going forward for those still eligible.
Not prefunded—benefits are paid directly by GE and are subject to company credit risk.
Must retire from GE to receive payments. No benefit is payable if you leave before retirement eligibility.
Benefits may be subject to forfeiture or reduction under certain separation or misconduct scenarios.
-
✅ Company Risk Matters
Since the ERB is unfunded and non-guaranteed, it’s subject to GE’s financial health. Factor in the company’s creditworthiness when projecting your long-term income.✅ Payout Structure is Unique
ERB may be paid as a lifetime annuity or as installments over 10 years—make sure your withdrawal strategy aligns with tax efficiency and longevity goals.✅ Timing of Retirement is Critical
Retiring from GE is key. Leaving early or accepting an outside offer may result in a complete loss of your benefit.✅ Coordinate With Other Retirement Income
The ERB stacks on top of your GE pension and PPA/VPA balances—use this to optimize drawdown strategies, minimize tax spikes, or delay Social Security.
For illustrative purposes only.
GE Executive Restoration Plan
The GE Restoration Plan is a nonqualified deferred compensation benefit designed to “restore” retirement contributions for employees whose compensation exceeds IRS limits under qualified plans. Because contributions to the GE Retirement Savings Plan (RSP) are capped at certain income levels, this plan ensures that highly compensated employees still receive comparable retirement benefits — though with different tax treatment and risks.
-
Eligibility: Typically applies to employees in Executive Band or higher, or those whose earnings exceed the annual IRS compensation cap under 401(a)(17). An executive eligible for the Executive Installment Benefit is not eligible for the Restoration Plan.
Contribution Formula:
7% of compensation above the IRS limit
Contributions made by GE — no employee deferral required
Vesting: Vests after 3 years of service above the IRS limit
Distribution:
Paid as a lump sum in the year following termination of employment
Subject to ordinary income tax (not eligible for rollover)
Subject to FICA tax at vesting
Tax Status:
Not tax-deferred in a traditional retirement plan sense
Nonqualified — not protected by ERISA or PBGC
Creditor Risk: As an unfunded corporate promise, benefits are subject to GE’s solvency
-
✅ Plan for a large income year — distributions post-termination may significantly spike taxable income
✅ Coordinate with other income sources (bonuses, RSUs, pensions) to manage tax brackets
✅ Watch for Medicare IRMAA thresholds — large distributions may increase premiums
✅ No rollover means you must be ready to absorb the full tax hit in one year
✅ Track vesting to ensure you’re eligible — leaving GE too early could result in forfeiture
✅ Evaluate concentration risk — this benefit is tied to GE’s long-term financial health
✅ Model post-exit liquidity needs — benefits may arrive before Social Security or pension elections kick in
Retirement Transition
Retiring From GE
Retirement from GE can happen through several distinct paths — each with different implications for your pension, retirement savings, health benefits, and taxes. Whether you're planning a Regular Retirement, exiting through a Voluntary Job Elimination (VJE), receiving a Special Early Retirement Option (SERO), or qualifying for Disability Retirement, understanding the rules and timing is critical to building a confident financial transition.
-
🟢 Regular Retirement
Eligibility: Typically age 60+ with sufficient years of service
Pension: Full benefits payable (depending on plan eligibility)
Savings Plan (RSP): In-service rollover or post-separation rollover to IRA
Insurance: Group life insurance may be eligible for conversion or portability
Healthcare: May qualify for retiree health coverage based on years of service
NQDC: Lump sum or installment payout, depending on plan elections
🟠 Voluntary Job Elimination (VJE)
What It Is: Structured severance during workforce reductions
Eligibility: Offered to selected employees during restructuring
Severance: Typically based on service years (e.g., 1–2 weeks per year)
Treatment: May be categorized as retirement if service and age criteria are met
Benefit Continuity: Pension and health benefits preserved if “retirement” status is confirmed
🔵 Special Early Retirement Option (SERO)
What It Is: Limited-time enhanced early retirement program
Eligibility: Often requires minimum age (e.g., 55) and service (e.g., 25 years)
Pension: May include early access with reduced or waived penalties
Healthcare: Often includes retiree health or subsidies
Election Window: Strict deadlines — often 30–60 days to respond
Appeal: Attractive for eligible employees not yet at full retirement age
⚫ Disability Retirement
What It Is: Retirement triggered by permanent disability before normal retirement age
Eligibility:
Must be approved through GE’s disability review process
Often requires vested service and disability status that qualifies under the pension plan
Pension: May become payable earlier under disability rules (varies by plan)
Healthcare: Continued access may be granted if receiving a GE disability pension
Savings Plan (RSP): Can roll over after separation; no early withdrawal penalty for IRS-defined disability
Taxation: Disability pension may be taxable as ordinary income
-
✅ Start benefit elections 60–90 days before exit — processing delays are common with pensions and healthcare transitions
✅ Track your retirement classification — “Retirement” status vs. “Termination” affects pensions, retiree health, and NQDC payouts
✅ Coordinate cash flow — match pension start date, RSP rollover, severance, and Social Security for seamless income
✅ Consider rolling over your RSP to an IRA — for broader investment access, lower-cost options, and better coordination with your withdrawal strategy
✅ Plan for a spike in taxable income — especially if severance, pension lump sum, RSUs, or NQDC hit the same year
✅ Disability retirees should understand:
Whether they’re receiving a disability pension or only LTD benefits
How this affects tax treatment, Medicare eligibility, and survivor options
✅ Review retiree health options — compare GE HRA eligibility, COBRA timing, Medicare enrollment, and private insurance
✅ Rebalance your portfolio — retirement often requires adjusting asset allocation, especially if overweight in GE stock
✅ Update estate documents — beneficiary designations, powers of attorney, and trusts should align with your retirement plan
About Stonehearth Capital
Stonehearth Capital is an independent, fiduciary, wealth management firm helping GE Aerospace employees and their family manage risk and identify opportunities for over 40-years.
Have A Question?
Send your question to: info@stonehearthcapital.com
Or, schedule a free 30-minute strategy call.
Disclosure: Stonehearth Capital Management is not affiliated with, endorsed by, or sponsored by GE Aerospace. We are an independent financial advisory firm that has experience working with GE Aerospace employees and their retirement benefits.